Every day, your lungs process about 11,000 liters of air to fuel your body with oxygen. Yet pollution, smoking, stress, and unhealthy diets can weigh them down, leaving you short of breath and vulnerable to illness. According to the World Health Organization, respiratory diseases are among the leading causes of poor health worldwide, with millions of people suffering from conditions like asthma, COPD, or chronic bronchitis.
Here’s the good news: what you eat can play a vital role in lung health. Certain foods contain antioxidants, anti-inflammatory compounds, and vitamins that not only protect lung tissue but may also help repair damage and improve breathing within days. While no single food can work miracles, adding the right nutrients consistently can create powerful changes in just a short time.
In this article, you’ll discover nine foods that support healthier lungs, how they work, and practical ways to add them to your daily routine. Whether you live in a polluted city, are recovering from smoking, or simply want to take better care of your lungs, these foods may help you breathe easier and feel stronger.
Why Food Matters for Lung Health
Your lungs are constantly exposed to oxygen, pollutants, and pathogens. Antioxidant-rich foods reduce oxidative stress, while anti-inflammatory nutrients protect delicate lung tissue. Vitamins and minerals play key roles in healing, circulation, and immunity. Unlike medications that often address symptoms, food offers a natural way to nourish the lungs from the inside out.
9 Foods That Improve Lung Health
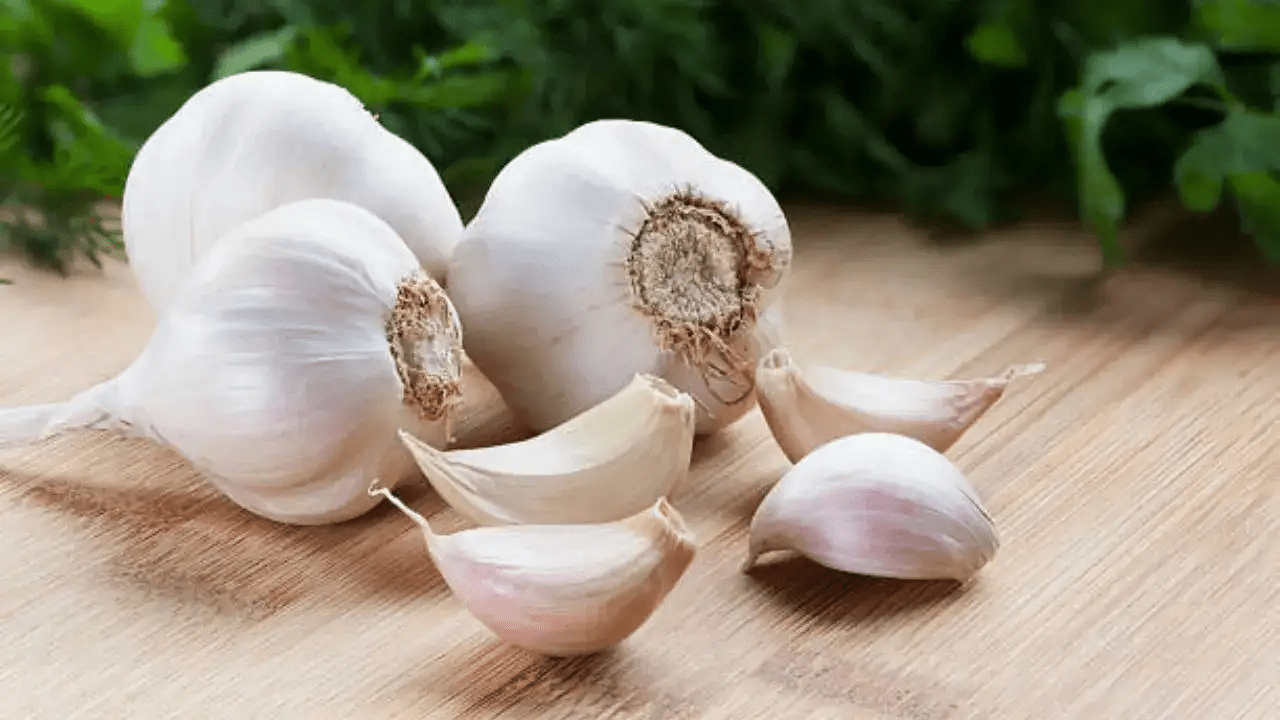
1. Garlic
Garlic is rich in allicin, a compound with antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. Studies show it can help reduce airway inflammation and support immunity, making it especially helpful for people with asthma or chronic bronchitis.
How to use: Add raw garlic to salads, or sauté lightly in meals to preserve its active compounds.

2. Ginger
Ginger contains gingerol, which relaxes airway muscles and improves circulation. It helps clear mucus and reduces congestion, making it a natural decongestant.
How to use: Drink ginger tea, or add grated ginger to soups and stir-fries.
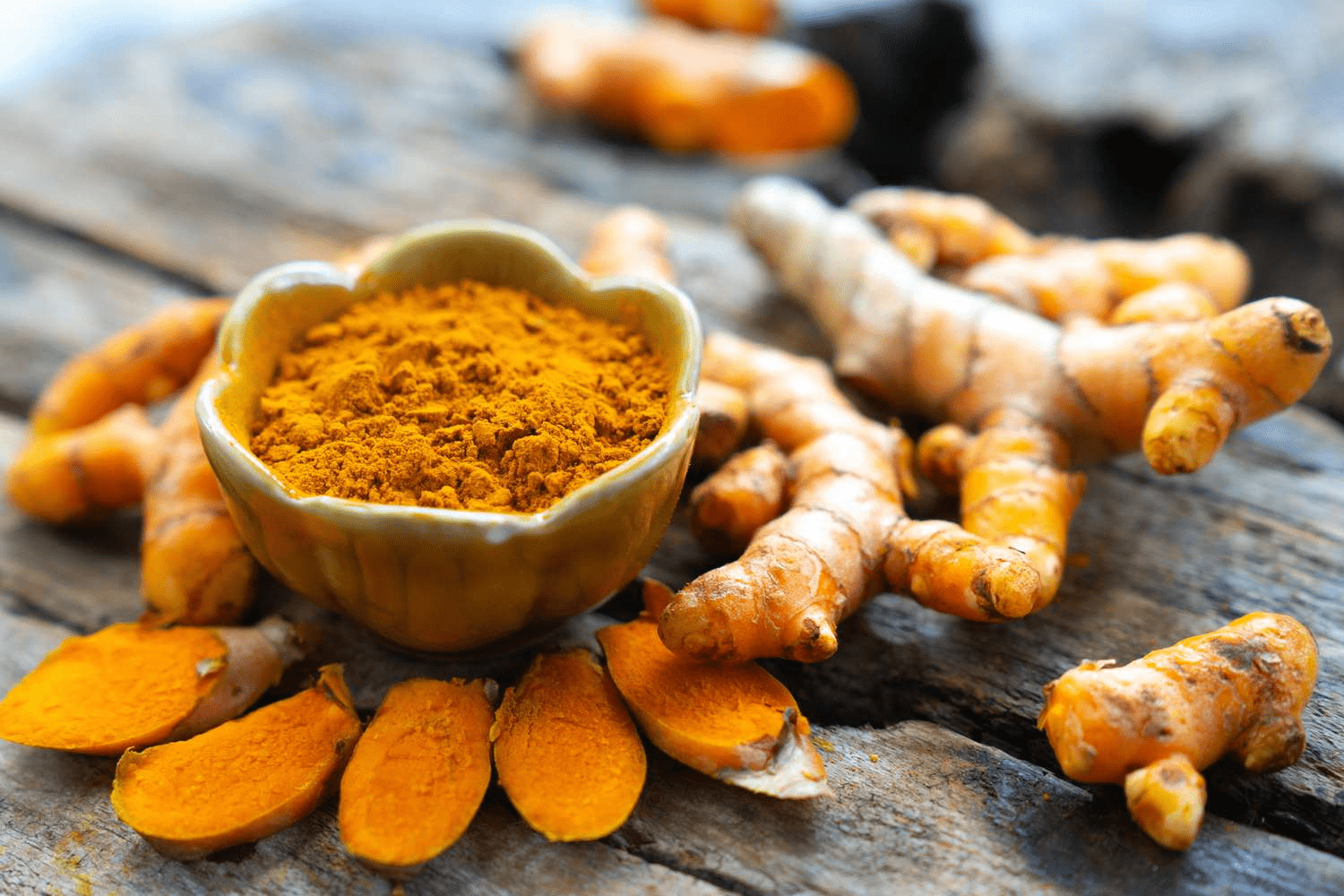
3. Turmeric
Curcumin, the active ingredient in turmeric, has powerful anti-inflammatory effects. It supports lung detoxification and may help reduce damage caused by pollutants.
How to use: Add turmeric to curries, golden milk, or smoothies.

4. Apples
“An apple a day” may be especially true for your lungs. Apples are rich in quercetin and vitamin C, which protect lung tissue from oxidative damage.
How to use: Eat fresh apples, blend into smoothies, or add slices to oatmeal.
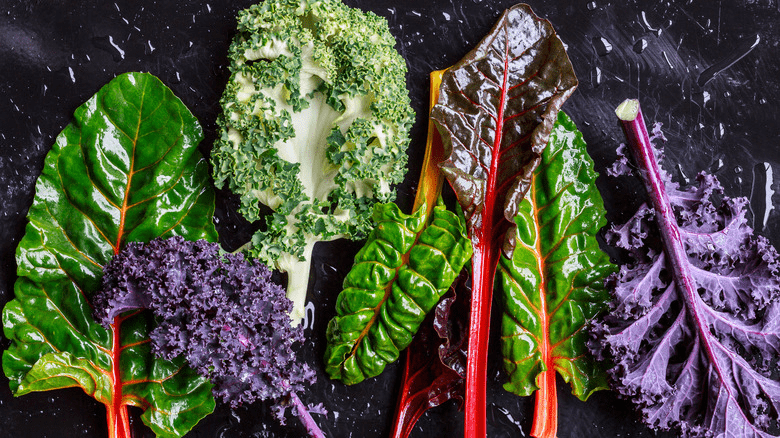
5. Leafy Greens (Spinach, Kale, Swiss Chard)
These greens provide chlorophyll, vitamin E, and magnesium, which improve oxygen transport and reduce inflammation. Magnesium is particularly important for people with asthma.
How to use: Add to salads, sauté lightly, or blend into green smoothies.

6. Fatty Fish (Salmon, Mackerel, Sardines)
Omega-3 fatty acids in fatty fish reduce inflammation and support cardiovascular health, which indirectly helps your lungs deliver oxygen more efficiently.
How to use: Grill salmon, add sardines to salads, or enjoy mackerel with whole grains.
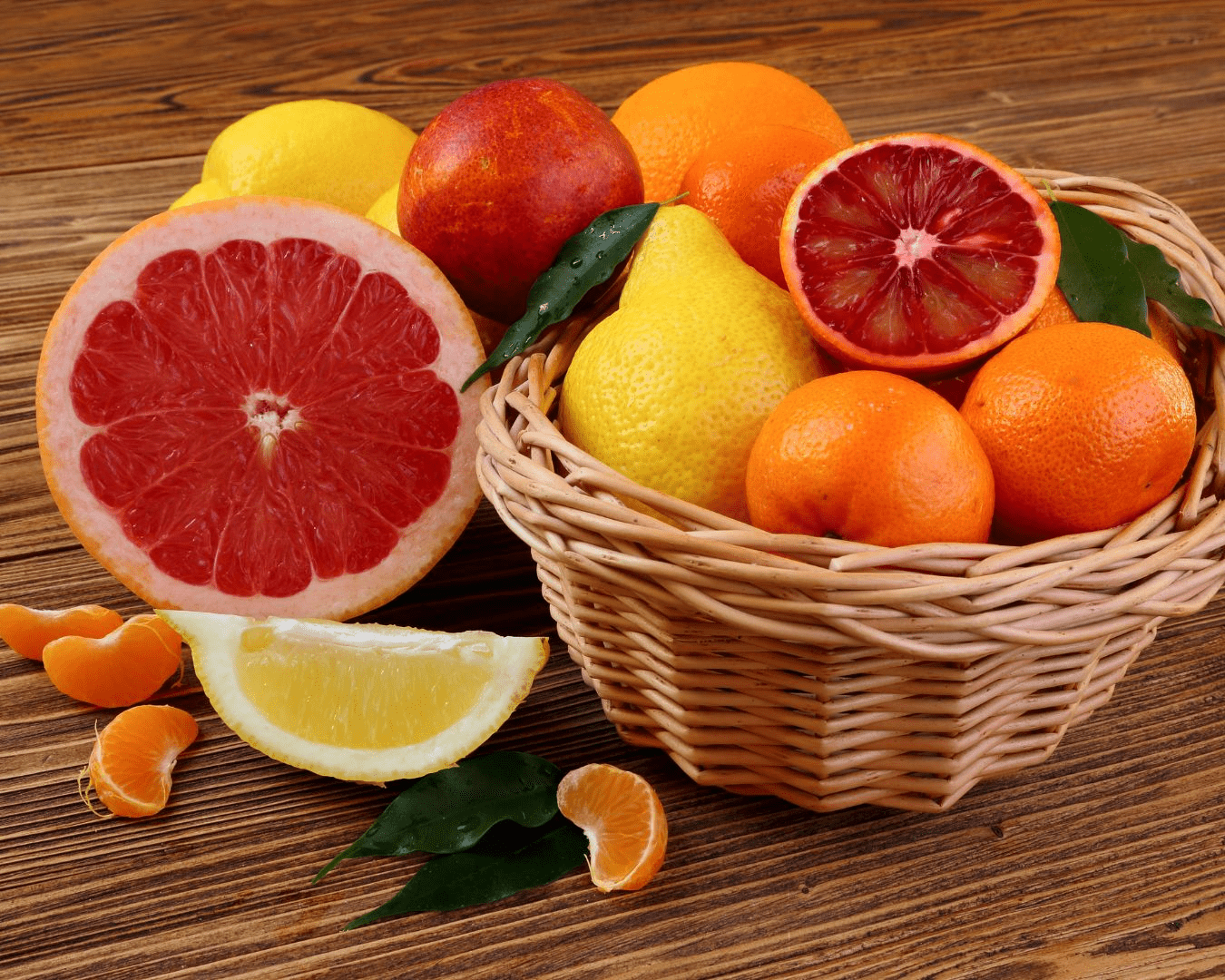
7. Citrus Fruits (Oranges, Lemons, Grapefruit)
Packed with vitamin C, citrus fruits strengthen immunity and improve collagen production in lung tissue. They also help neutralize free radicals caused by pollution.
How to use: Drink fresh orange juice, or squeeze lemon over salads and seafood.

8. Nuts and Seeds
Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are rich in vitamin E and healthy fats. Vitamin E is an antioxidant that helps protect lung tissue and maintain elasticity.
How to use: Snack on a handful of nuts, sprinkle seeds into yogurt, or add to smoothies.
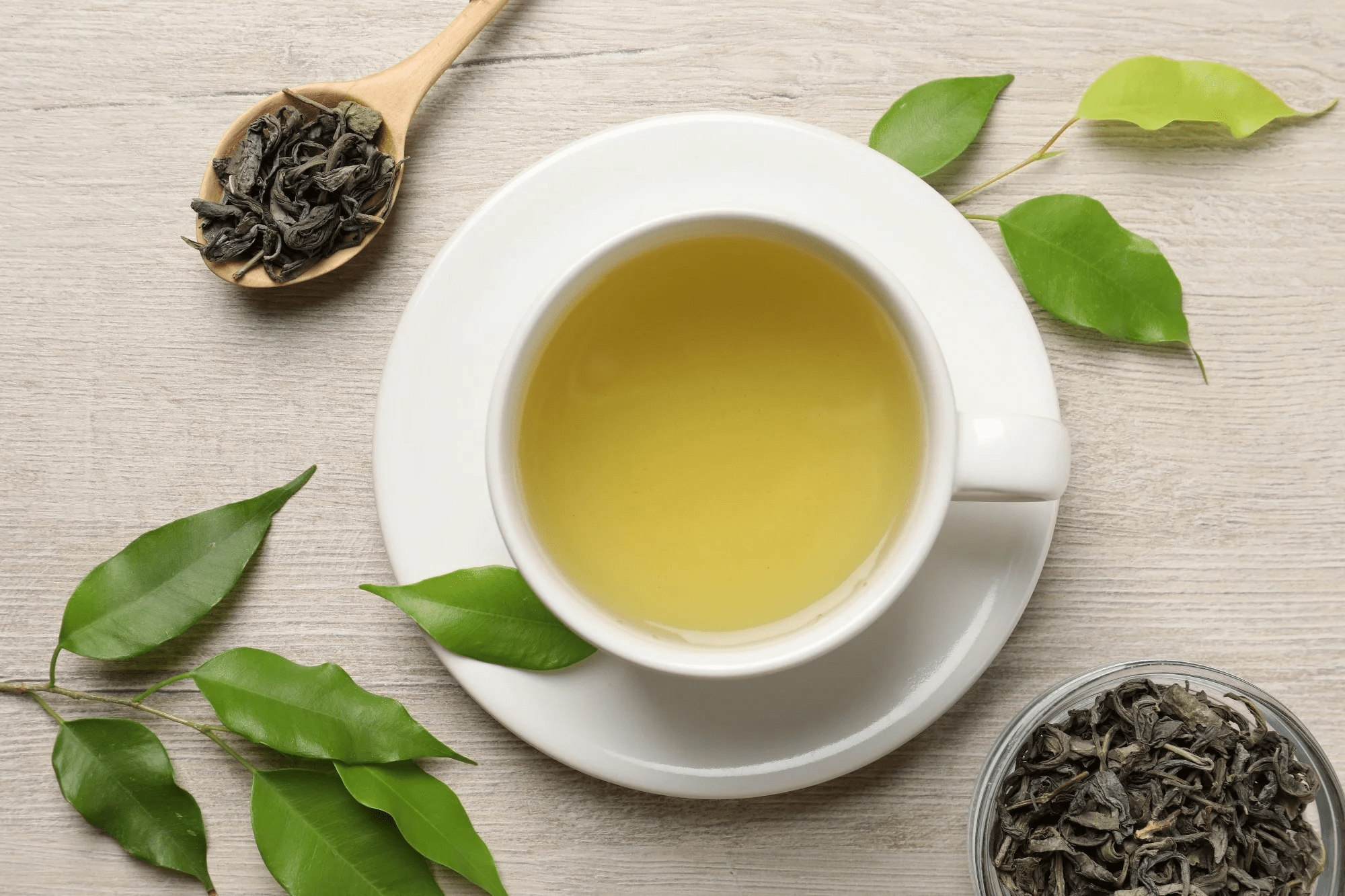
9. Green Tea
Green tea contains catechins and theophylline, which help relax airways, reduce inflammation, and protect against lung cancer.
How to use: Drink 1–2 cups daily, preferably without sugar.

Quick Reference Table
| Food | Key Nutrient | Lung Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Garlic | Allicin | Reduces airway inflammation |
| Ginger | Gingerol | Clears mucus, decongestant |
| Turmeric | Curcumin | Anti-inflammatory, detox |
| Apples | Quercetin, Vitamin C | Protects lung tissue |
| Leafy greens | Chlorophyll, Magnesium | Oxygen transport, anti-asthma |
| Fatty fish | Omega-3s | Reduces inflammation |
| Citrus fruits | Vitamin C | Immunity, tissue repair |
| Nuts & seeds | Vitamin E | Protects lung elasticity |
| Green tea | Catechins | Relaxes airways, anti-cancer |
Real-Life Examples
- Case 1: Former Smoker’s Recovery
A man in his 50s recovering from smoking added garlic, apples, and green tea to his daily diet. Within three weeks, he noticed reduced coughing and better breathing capacity. - Case 2: Asthma Management
A teenage girl in a polluted city improved her diet with spinach, fatty fish, and citrus fruits. She reported fewer asthma flare-ups and improved stamina. - Case 3: Everyday Wellness
A health-conscious mother incorporated ginger tea and turmeric smoothies into her family’s routine. They experienced fewer colds and improved energy during flu season.
Lifestyle Tips to Support Lung Health
- Stay hydrated to thin mucus and improve breathing.
- Practice deep breathing exercises to expand lung capacity.
- Avoid smoking and secondhand smoke.
- Exercise regularly to strengthen lung function.
- Pair healthy foods with antioxidant-rich spices like cinnamon and cloves for added benefits.
Conclusion
Your lungs work tirelessly every day, yet most of us take them for granted until problems arise. By adding garlic, ginger, turmeric, apples, leafy greens, fatty fish, citrus fruits, nuts, and green tea to your diet, you give your lungs the nutrients they need to heal, detoxify, and perform at their best.
Quick FAQ
- Can food really improve lung health in 3 days? While results vary, adding lung-friendly foods can reduce inflammation and improve breathing quickly.
- Do I need to eat all nine foods daily? No, but a combination over the week will maximize benefits.
- Are supplements as effective as whole foods? Whole foods provide better absorption and added nutrients.
- Can diet replace medicine? No, but it can complement treatments and improve overall lung resilience.
This article is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare provider before making major dietary changes or managing chronic conditions.